Temporal Artery Biopsy
Your doctor has recommended a temporal artery biopsy. This page will explain: What temporal arteritis is Why you might need this test How the test is done What happens afterwards Please ask your doctor if you have any questions.
What is Temporal Arteritis (TA)?
Temporal arteritis (also called giant cell arteritis) is a condition where the arteries in your head, especially around your temples, get swollen and inflamed.
- It mostly happens in older people, usually over 50 years of age.
- We don't know exactly what causes it.
- If not treated quickly, it can sometimes lead to blindness or stroke.
Symptoms
- Headache usually on one or both sides of your head, around your temple
- Tender scalp
- Jaw pain when chewing
- Fever, tiredness, weight loss
- Vision problems such as double vision or blurriness
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is usually suspected because your doctor has recognised the typical collection of symptoms and clinical signs. Blood tests are taken to check for inflammation. However, these tests are not specific for TA.
An ultrasound scan of the temporal artery can be performed but in some cases a biopsy of the temporal artery is also needed.
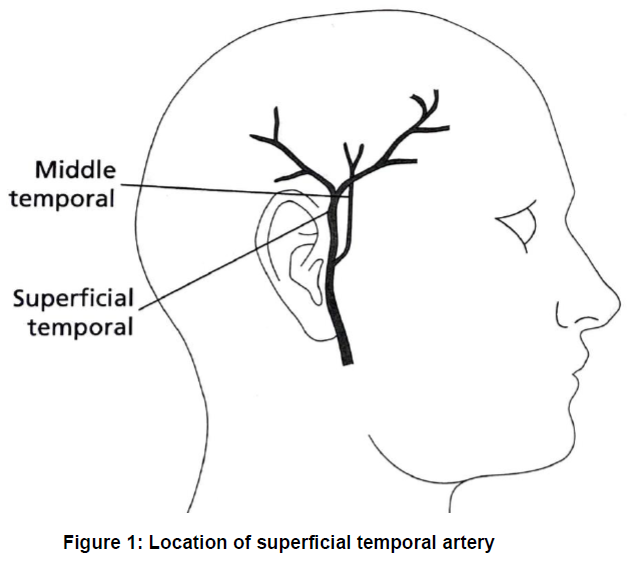
The superficial temporal artery is a blood vessel close to the skin that can be felt on both temples located on either side of the head (see picture below).
Why do I need a temporal artery biopsy?
The temporal artery biopsy may help your medical team decide whether you have temporal arteritis. A temporal artery biopsy will also help determine the medication you need to take and whether you will need to take medication long term. In some cases where suspicion of TA is high, we may treat you with medication even if the biopsy is negative or inconclusive.
What are the benefits?
The aim of the biopsy is to take a small piece (1 to 2 cm long) of one of the temporal arteries (see Figure 1) which will be studied under a microscope. If there are signs of inflammation in keeping with temporal arteritis, this will confirm the diagnosis.
Knowing for sure will help your doctor decide which medicine is best for you.
What are the risks?
The risks of temporal artery biopsy are uncommon but could include:
- Infection in the wound requiring a course of antibiotics.
- Scarring - the wound is often hidden in a skin fold or the hairline to reduce any obvious scar. Hair may not regrow around the wound site.
- Problems with the blood circulation to the skin and scalp can lead to an ulcer (non-healing area).
- The sample may not give an answer (non-diagnostic) and your medical team may discuss with you the need to perform another biopsy.
- Nerve damage. This can lead to numbness or weakness on the same side of the face as the artery being sampled. This may or may not recover over time.
- Stroke is an extremely rare complication of TA. There has been a reported incidence of stroke in the literature following this procedure in someone with confirmed TA.
Is there an alternative?
Sometimes a doctor can use a special scan to look at your arteries instead.
You do not have to have this procedure but it will make it more difficult to find the cause of your symptoms.
The surgery
We perform most temporal artery biopsies under local anaesthetic. This means that you are awake during the procedure. You will not be able to feel any pain after having the local anaesthetic but you may still feel pressure and movement.
The effects of the local anaesthetic will last for several hours, until the medication wears off.
If you are having a local anaesthetic, you will be able to eat and drink normally before the procedure.
The biopsy will take between 45 minutes to 1 hour to perform.
You will have stitches at the wound site. You will be told by your surgeon if the stitches require removal by the practice nurse at your GP’s surgery.
Aftercare
You will need to keep the wound clean using a cotton bud dipped in boiled cooled water.
Keep the wound dry for 7 days.
You may be given an antibiotic ointment to use on the wound for 7 days.
You may also need to make an appointment with the practice nurse at your GP’s surgery to have the stitches removed after 7 days.
You may be able to work the following day depending on your occupation. Please discuss this with your surgeon prior to the procedure.
If you have pain, discharge or swelling at the biopsy site, please contact the ENT department. The number is at the end of this page. Out of hours please go to the nearest Accident & Emergency Department.
Results
You will be contacted via letter by your medical team with the results of the biopsy within 6 weeks of your surgery.